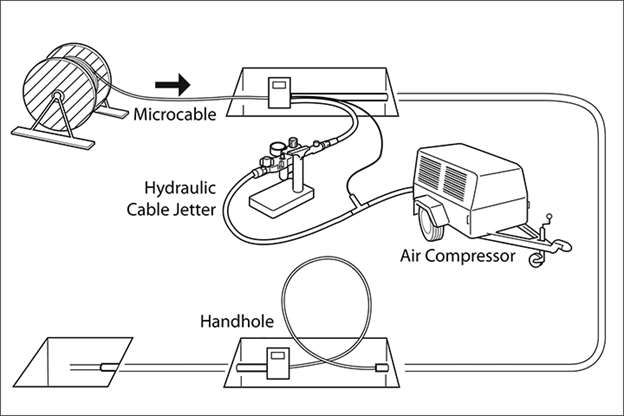
The Air Blown Fiber System
The Air Blown Fiber (ABF) was developed to give technicians an easier method to install cables, in order to reduce the costs of installation and to increase the flexibility in the design of networks. This system uses small ducts, the micro ducts, that are used to blow the bundle of fibers inside them, using compressed air. These bundles of fibers are lightweight, easy to transport and store. The microducts bundles can be easily split and it’s possible to drive each one, to a different route. The fibers can be blown using these tubes, to facilitate the distribution without splicing and creating a point to point installation.
The air blown system makes the fibers “fly” inside the micro duct, never touching the walls of the duct. This reduces friction and allows the installation of several kilometers without interruptions.
Main advantages of the air blown fiber system
Flexibility
The main advantage of using an air blown fiber cable is the flexibility. If the technology changes and we need to change the type of fibers deployed, we simply have to pull out the existing fibers and blow the new type in the same microducts. In the same way, we can install bundles of 24 fibers, and, when needed, install another 24 in the same microduct without disruption on the services installed.

Cost of installation
The cost of installing air blown fiber cables is more or less the same as the traditional cable. The fibers and the microducts may be more expensive than the traditional cables but the lower numbers of splices required in the ABF system and the deployment will balance the costs in the end.
The main advantage in terms of costs, is the capacity to deploy more fibers in the same tubes if needed. For example, if it’s needed to replace the fiber technology to a new one.

Air blown fiber cable or Traditional cables?
The air blown fiber cable system is more flexible but whenever we need to increase the number of fibers deployed, a team of technicians checks if the tubes don’t have any blockage. The technician must blow the new fibers to the tube and do the necessary splicing and connectorization. For that reason, there is always a risk of damage to the other fibers, that were previously installed in the same tube. If it’s possible to plan the future needs, a traditional cable with enough reserves will be more cost effective and secure. The space that the air blown fiber cable use in the main ducts, is a big disadvantage of this system. It´s possible to have six times more fibers in the same space using the traditional cables, allowing better use of these main ducts.
Air blown fiber cable
The ABF is recommended where it’s planned to add or change frequently the network, and when the count number of fibers is not too large. It is also a very good choice for the last mile of an FTTH deployment, where the cost, flexibility and speed of installation are very important.
Traditional cable
In what comes to the traditional cables, they are more suitable for Trunk Networks, that can be planned, when the space in ducts is of extreme importance, and when the number of fibers can easily reach 144, 288 or more.